
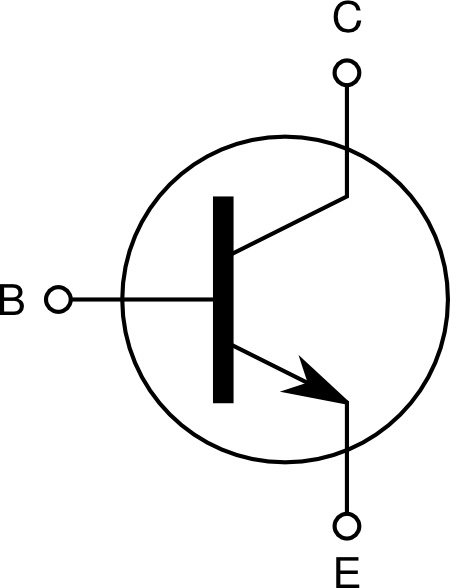
Collector current is dependent on the base current.Ģ. A transistor in the active region is used for amplification. Active region: In this region, the emitter-base region is forward biased and collector-base junction is reverse biased. The following table shows the different regions of operations on different biasing configurations. On the basis of the biasing transistor operates in the three different regions. When we apply external voltage supply to the transistor this process is known as the biasing of the transistor. 1.2 Transistors symbols Transistor Action In PNP transistor arrow shows the direction from p terminal to n terminal so the flow of current is from the emitter to base.In NPN transistor arrow shows the direction from p terminal to n terminal so the flow of current is from the base to emitter.Arrow is always present on the emitter terminal and the direction of the arrow represents the flow of current due to charge carriers. Transistor Symbolsįig 1.2 shows the symbols representation of NPN and PNP transistors. NOTE: When two practical diodes are connected back to back, it can’t work as a transistor because there is no bonding force in between the two diodes. (AREA) COLLECTOR > (AREA) EMITTER > (AREA) BASE (DOPING) EMITTER > (DOPING) COLLECTOR > (DOPING) BASE Collector area is larger than the emitter and base area. The doping level of a collector is lying between the doping level of emitter and base. Collector is the other side of the transistor which collects the charge carriers. It is a lightly doped region of the transistor.ģ. The base-collector region is always reverse biased so it offers a high resistive path for the collector circuit. The base-emitter region is always forward biased so it offers a very low resistive path for the emitter circuit. Base is the middle thin region of a transistor. The emitter-base junction is always forward biased so that it can supply large numbers of majority charge carriers to the Base. Emitter is responsible to supply charge carriers (NPN-electrons or PNP-holes) in the transistor. 1.1 Basic Construction of TransistorĪ transistor (NPN or PNP) consist of three regions of doped semiconductors, which are named as Emitter, Base and Collector.ġ. In NPN transistor charge carriers are electrons. It is shown in fig 1.1.Ī transistor in which a thin layer of p-type semiconductor is sandwiched between two layers of n-type semiconductor is known as NPN transistor. In PNP transistor charge carriers are holes. A transistor is classified into two types based on its construction.Ī transistor in which a thin layer of n-type semiconductor is sandwiched between two layers of p-type semiconductor is known as PNP transistor. Basic Construction of BJTĪ BJT consists of two pn junctions so it is analogous to two back to back connected diodes as shown in fig 1.1. Note: The usage of the term transistor in this article will be used for bipolar junction transistor (BJT).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
